Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is the Balanced Scorecard?
- 3. Key Components of the Balanced Scorecard
- 4. The Importance of Strategic Planning
- 5. Turning Strategy into Reality
- 6. Implementing the Balanced Scorecard
- 7. Benefits of Using the Balanced Scorecard
- 8. Common Challenges and Solutions
- 9. FAQs
- 10. Conclusion
1. Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations face relentless pressure to perform and deliver results. One of the most effective methods for translating vision into actionable strategies is through the Balanced Scorecard (BSC). This strategic planning tool allows leaders to align their business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization, improve internal and external communications, and monitor organizational performance against strategic goals.
2. What is the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management framework developed by Dr. Robert Kaplan and Dr. David Norton in the early 1990s. Unlike traditional performance measurement systems, the BSC encompasses not only financial measures but also operational, customer, and learning and growth perspectives. By taking a balanced approach, it fosters a more holistic view of organizational health and performance.
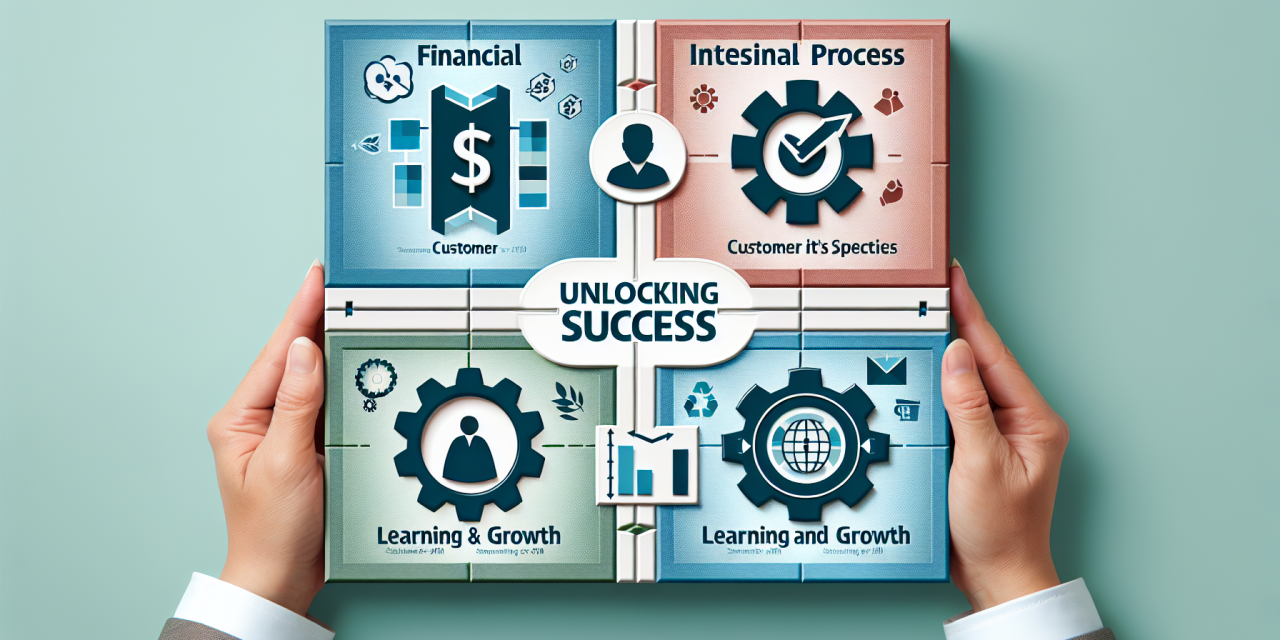
2.1 The Four Perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard
The BSC consists of four key perspectives that provide a comprehensive view of organizational performance:
- Financial Perspective: This dimension addresses the financial performance of the organization, focusing on metrics such as revenue growth, profitability, and cost management.
- Customer Perspective: This perspective emphasizes customer satisfaction and loyalty, helping organizations understand how their customers view their products and services.
- Internal Business Processes Perspective: Here, organizations analyze the efficiency and effectiveness of their internal processes, which directly contribute to customer satisfaction and financial performance.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: This dimension highlights the importance of employee training, culture, and knowledge management as catalysts for organizational improvement.
3. Key Components of the Balanced Scorecard
When implementing the Balanced Scorecard, several key components come into play:
- Objectives: Clear objectives define what an organization aims to achieve across the four perspectives.
- Measures: These are quantifiable metrics that allow organizations to assess their performance against objectives.
- Targets: Setting specific targets helps organizations drive performance toward desired outcomes.
- Initiatives: These are actions and projects that organizations undertake to reach their strategic goals.
4. The Importance of Strategic Planning
Strategic planning addresses the need for businesses to be proactive rather than reactive in today’s competitive landscape. It serves as a roadmap, guiding organizations on how to allocate resources effectively, respond to market dynamics, and achieve their long-term goals.
4.1 Aligning Resources
By clearly defining priorities through strategic planning, organizations can align resources to ensure that every effort contributes to overarching goals. This alignment enhances operational efficiency, leading to better resource utilization.
4.2 Adapting to Change
With rapid changes in technology and market conditions, businesses must remain agile. A solid strategic plan, supported by the Balanced Scorecard, equips organizations to adapt swiftly to new challenges. In fact, exploring the Balanced Scorecard & Strategic Planning Training Course can provide valuable insights into how to navigate such transitions effectively.
5. Turning Strategy into Reality
Organizations often struggle to execute their strategies due to a lack of clarity or consistent focus. Here, the Balanced Scorecard plays a crucial role by translating strategic plans into tangible actions.
5.1 Communicating the Strategy
Effective communication is vital for success. The Balanced Scorecard helps leaders convey their strategic vision to the entire organization, ensuring that all employees understand the company’s direction and their roles in achieving results.
5.2 Monitoring Progress
Regular tracking of performance metrics enables organizations to identify areas that need attention. This proactive monitoring fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement, helping teams stay aligned with strategic objectives.
6. Implementing the Balanced Scorecard
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard requires a structured approach to ensure its effectiveness. Here are the key steps:
- Step 1: Vision and Strategy Development: Define the long-term vision and strategic objectives of the organization.
- Step 2: Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Determine the metrics that will measure success across the four perspectives.
- Step 3: Strategy Mapping: Create a visual representation of the strategy and how different objectives interlink.
- Step 4: Communication and Training: Train employees and communicate the strategy to ensure alignment and understanding.
- Step 5: Monitor and Adapt: Regularly review performance and make necessary adjustments to the strategy.
7. Benefits of Using the Balanced Scorecard
Integrating the Balanced Scorecard into your strategic planning process yields numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Clarity: It provides a clear framework, enabling organizations to articulate their strategy effectively.
- Improved Performance: The focus on measurable outcomes encourages operational excellence and fosters continuous improvement.
- Alignment Across the Organization: By aligning all levels of the organization with strategic objectives, everyone works towards common goals.
- Increased Accountability: The BSC holds teams accountable for their contributions to strategic objectives, creating a culture of responsibility.
8. Common Challenges and Solutions
While the Balanced Scorecard offers significant advantages, organizations may face challenges during its implementation. Here are some of the most common hurdles and how to overcome them:
8.1 Lack of Leadership Support
Without strong leadership endorsement, implementing the Balanced Scorecard may falter. To address this, involve leaders early in the process and demonstrate how the BSC aligns with organizational goals.
8.2 Inadequate Training and Understanding
Many employees may struggle to grasp the Balanced Scorecard and its importance. Offering comprehensive training programs, such as exploring a comprehensive guide to mastering strategic planning using the Balanced Scorecard, can empower teams to effectively utilize the framework.
9. FAQs
9.1 What industries benefit from the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is adaptable to various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, education, and non-profits. Organizations of all sizes can leverage its principles to enhance their strategic management.
9.2 How often should organizations review their Balanced Scorecard?
Organizations should conduct regular reviews of their Balanced Scorecard, ideally quarterly. This frequency allows for timely identification of performance gaps and the opportunity to adjust strategies accordingly.
9.3 Can the Balanced Scorecard be applied at different organizational levels?
Absolutely! The Balanced Scorecard can be implemented at organizational, departmental, and individual levels, ensuring alignment across all facets of the organization.
9.4 How does the Balanced Scorecard enhance communication?
By providing a common language for discussing strategy, the Balanced Scorecard enhances communication among teams. It enables everyone in the organization to understand how their roles contribute to overall success.
10. Conclusion
To summarize, the Balanced Scorecard is an invaluable tool that empowers organizations to turn strategy into reality. By providing clarity, fostering alignment, and driving accountability, it enhances overall performance and adaptability.
When strategically implemented, the Balanced Scorecard can serve as a roadmap, guiding organizations toward sustainable success. To learn more about integrating the Balanced Scorecard into your strategic planning, consider exploring resources like the enhancing personal leadership skills and the mastering project management principles. By adopting this approach, your organization will be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape.