Table of Contents
- What is HACCP?
- The Importance of HACCP
- Principles of HACCP
- Evolving Knowledge Through Training
- Implementing a HACCP System
- Challenges in HACCP Implementation
- Benefits of a Robust HACCP System
- FAQs about HACCP
- Conclusion
What is HACCP?
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a management system designed to ensure food safety through the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards. This systematic approach emphasizes verification, monitoring, and record-keeping which adds a layer of accountability and quality assurance within food handling and processing environments.
The Importance of HACCP
In today’s rapidly evolving food industry, prioritizing safety becomes not just a choice but a necessity. HACCP plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health. By identifying potential hazards at various points in the food production process and implementing changes before they escalate, businesses take significant steps in preventing foodborne illnesses.
Safeguarding Public Health
The primary goal of HACCP is to protect consumers from foodborne illnesses. With the rise of global food distribution, the need for food safety management systems has become critical. Consequently, proper training in HACCP principles ensures that personnel are equipped to maintain high safety standards.
Regulatory Compliance
Furthermore, compliance with local and international food safety regulations has grown increasingly stringent. Companies that implement effective HACCP systems increase their chances of meeting these requirements, thereby avoiding potential fines and legal issues.
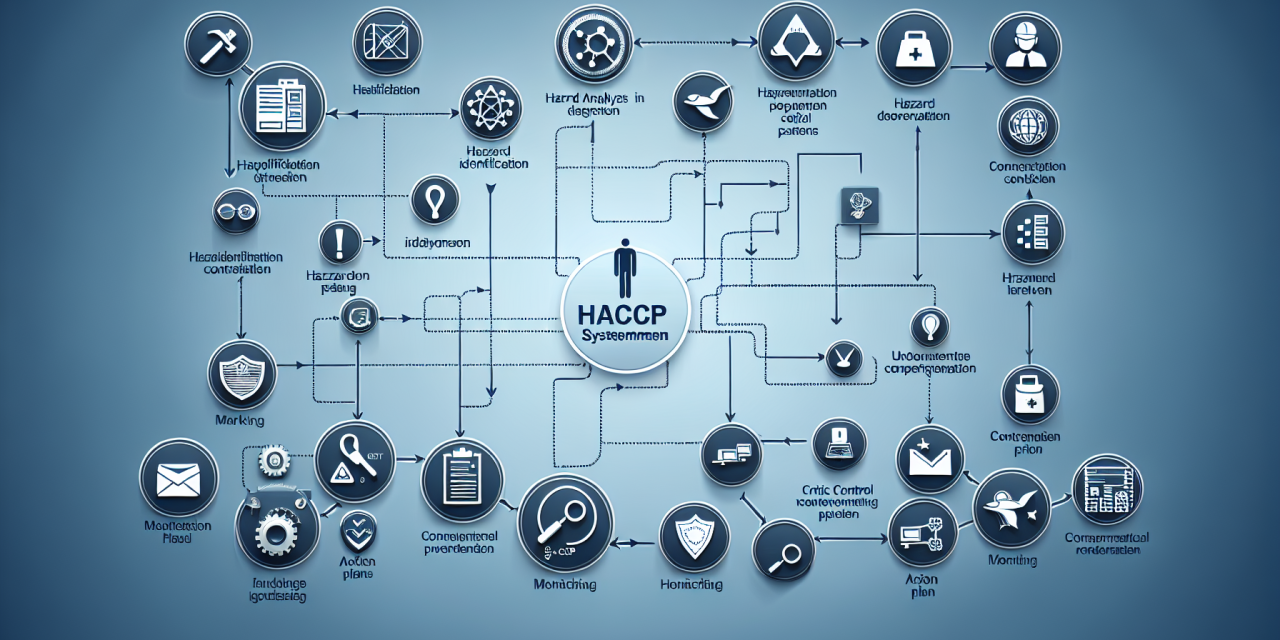
Principles of HACCP
Understanding HACCP involves familiarization with its seven core principles:
- Conduct a Hazard Analysis: Determine what hazards could potentially occur in the food production process.
- Identify Critical Control Points (CCPs): Find the points in the process where controls can be applied to prevent, eliminate, or reduce food safety hazards.
- Establish Critical Limits: Set the maximum or minimum limits for each CCP to ensure food safety.
- Establish Monitoring Procedures: Implement procedures for monitoring CCPs to ensure they stay within established limits.
- Establish Corrective Actions: Determine actions to take when monitoring indicates a CCP is not under control.
- Verify HACCP System: Establish procedures to verify that the HACCP system is working properly.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of monitoring, corrective actions, and verification activities.
Evolving Knowledge Through Training
Education on HACCP principles is essential for all industry professionals involved in food safety. Training employees on these principles cultivates a culture of safety where everyone understands their role in maintaining compliance.
Enhancing Skills and Knowledge
Undoubtedly, continuous professional development ensures that staff remain knowledgeable about evolving regulations and the latest food safety practices. This commitment to training directly enhances the overall safety culture within an organization.
Adopting a Proactive Approach
Moreover, adopting a proactive stance toward education fosters an environment of vigilance and responsiveness. Rather than merely reacting to issues as they arise, those trained can anticipate them, thereby minimizing risk.
Access to Resources
One excellent resource for comprehensive training in HACCP is the HACCP Food Safety Control Management Training Course, which provides learners with valuable insights into the principles and application of HACCP in their workplaces.
Implementing a HACCP System
Once trained, organizations must successfully implement HACCP principles to ensure long-term safety and compliance. This implementation process involves several key steps:
Forming a HACCP Team
A dedicated team should be established to facilitate the transition to a HACCP system. This team can ensure varied perspectives from across the business and contribute to well-rounded practices.
Conducting Hazard Analysis
The team must thoroughly assess potential hazards in food production and determine points of control. Identifying these hazards sets the foundation for an effective system.
Documentation and Training
Documenting each step of the development process enhances accountability within the organization. Additionally, comprehensive training for employees on the new system reinforces its importance.
Challenges in HACCP Implementation
Although implementing a HACCP system brings numerous benefits, several challenges can hinder effective execution:
Resistance to Change
Often, organizations face resistance from employees who are accustomed to traditional operating procedures. Addressing this resistance through clear communication and tailored training sessions can ease the transition.
Resource Allocation
Additionally, dedicating sufficient resources and time for implementation may pose difficulties for many businesses. However, investing in HACCP can result in greater long-term savings by preventing costly food safety incidents.
Benefits of a Robust HACCP System
Implementing a HACCP system offers numerous advantages, including:
Enhanced Food Safety
The most significant benefit remains the continual enhancement of food safety measures. Organizations can substantially reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses by following HACCP principles.
Improved Reputation
Furthermore, businesses that prioritize food safety cultivate stronger reputations within the industry and among consumers. Stakeholders increasingly value transparency and accountability.
Operational Efficiency
Lastly, HACCP fosters greater operational efficiency. Streamlining processes helps organizations run more smoothly, resulting in cost savings and enhanced productivity.
FAQs about HACCP
What industries must implement HACCP?
HACCP principles apply to various sectors, including but not limited to food manufacturing, catering, and food service establishments. Any industry involved in food handling can benefit from implementing HACCP.
How often should a HACCP plan be reviewed?
A HACCP plan should undergo regular reviews and updates, particularly when new hazards are identified or production processes change. Annual reviews are common, but more frequent assessments may be warranted.
Is HACCP the same as ISO 22000?
While both HACCP and ISO 22000 focus on food safety management, HACCP is a specific risk management system, while ISO 22000 incorporates HACCP principles within a broader management framework. Many organizations utilize both in tandem.
What is the relationship between training and compliance?
Training forms the backbone of compliance with HACCP regulations. By equipping staff with knowledge and skills needed to implement HACCP effectively, organizations significantly enhance their ability to meet compliance standards.
Conclusion
In summary, establishing a HACCP system is not merely a good practice in the food industry; it is essential for ensuring safety and compliance. With robust training, a committed team, and clear documentation, businesses can build an effective food safety management program. This investment not only fosters a culture of safety but also enhances overall efficiency and reputation in the market. By embracing HACCP principles, organizations take proactive steps in safeguarding public health while ensuring their operational success.
For more insights into training for safety culture, check out Building a Robust Safety Culture: Key Strategies for Effective Training. To understand safety compliance better, visit Navigating Safety Compliance and Site Inspections: A Pathway to a Safer Workplace. For an essential guide to process safety management, refer to Essential Guide to Effective Process Safety Management Compliance Training. Moreover, to explore best practices for safety in the oil and gas industry, you can access Enhancing Operational Safety in the Oil & Gas Industry: Strategies and Best Practices. Finally, to unlock benefits of advanced safety management training, take a look at Unlocking the Benefits of Advanced Health and Safety Management Training: A Roadmap to Workplace Excellence.