Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Confined Space?
- Why Are Confined Spaces Dangerous?
- Confined Space Regulations
- Key Safety Practices for Confined Space Entry
- Emergency Response Planning
- Training and Awareness
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Introduction
Regarding workplace safety, understanding confined space awareness and compliance is crucial. Confined spaces can pose serious risks, and awareness can prevent tragedies. Many workplaces require personnel to enter these hazardous areas, thus emphasizing the need for education and practical knowledge around safe entry procedures. Ultimately, this ensures that workers remain safe while efficiently completing their tasks.
What is a Confined Space?
A confined space refers to an area that is large enough for a worker to enter but has limited means of egress. Interestingly, these spaces are not designed for continuous occupancy. Common examples include tanks, silos, vaults, and pits. Due to their unique characteristics, confined spaces often pose multiple hazards, making caution imperative.
Types of Confined Spaces
In practice, confined spaces fall into several categories:
- Fully Enclosed: These spaces have limited access points and are entirely surrounded by walls or barriers.
- Partially Enclosed: While these spaces may have openings, they can still present hazards due to their structure.
- Workspaces under specific conditions: When work is performed in these spaces, they can transition from non-hazardous to hazardous.
Why Are Confined Spaces Dangerous?
Confined spaces can harbor a variety of dangers that make work inside them risky. First and foremost, they often contain hazardous atmospheres. Example: Toxic gases, low oxygen levels, or flammable vapors can develop in these areas. Consequently, understanding these risks is essential.
Common Hazards in Confined Spaces
- Chemical Exposure: Chemicals can accumulate, posing serious health risks.
- Physical Hazards: Examples include moving machinery or equipment, which can increase the potential for accidents.
- Environmental Factors: For instance, extreme temperatures or floods can create unsafe conditions within confined spaces.
Confined Space Regulations
Several regulations govern working in confined spaces. In many countries, health and safety administrations provide guidelines to ensure that both employers and employees understand and adhere to these laws. For example, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) outlines requirements for safer practices during confined space work. As such, awareness of local laws is crucial.
Key Safety Practices for Confined Space Entry
To ensure safe entry into confined spaces, several practices stand out:
1. Perform a Hazard Assessment
Before any work begins, conduct a thorough assessment of the confined space. Identify potential hazards, evaluate entry conditions, and determine necessary precautions. Engage with all team members in this process since diverse perspectives can enhance safety measures.
2. Develop an Entry Plan
Creating a detailed entry plan is vital. This document should outline the entire process, including roles, responsibilities, and necessary equipment. When everyone understands their tasks clearly, the team can work cohesively and reduce the chance of accidents.
3. Ensure Proper Training
Training is essential for all personnel involved in confined space entry. Regular training sessions keep everyone informed about the latest safety measures and create a culture of safety. Additionally, consider attending events like the Safe Confined Space Entry, Awareness & Compliance Conference to gain insights.
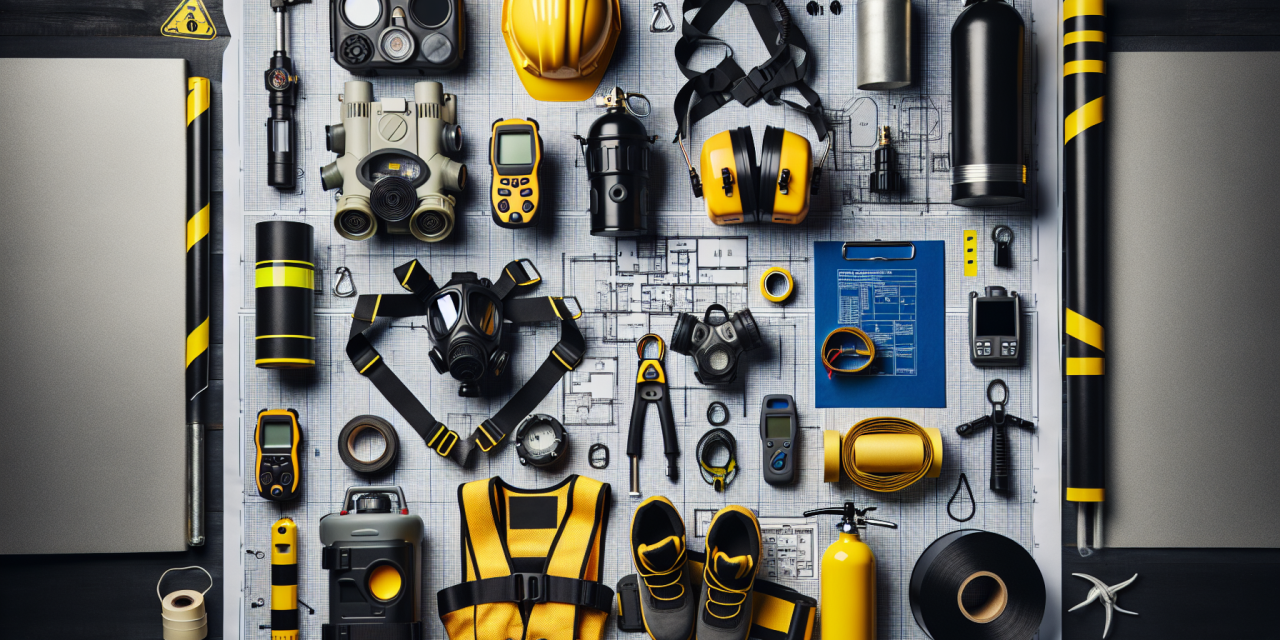
The Importance of Equipment
Utilize appropriate equipment for confined space entry. Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as helmets, gloves, and respiratory gear are crucial in protecting workers from potential hazards.
4. Monitor Atmospheric Conditions
Continuous atmospheric monitoring is necessary to ensure safe conditions. Implementing gas detection systems can provide real-time data on air quality within the space. If a hazardous condition arises, personnel should be prepared to evacuate immediately.
5. Establish Communication
Effective communication is vital during confined space operations. Establish a reliable method for workers to communicate while inside. This could be as simple as two-way radios or pre-arranged signals. Furthermore, maintain clear communication with those outside the confined space.
6. Require a Standby Person
A standby person must be present outside the confined space at all times. Their role includes monitoring the situation and initiating emergency response measures if needed. Their presence adds a critical layer of safety during the process.
Emergency Response Planning
Despite meticulous preparations, accidents can happen. Therefore, establish a comprehensive emergency response plan before any work occurs. This plan should outline how to respond to various scenarios, ensuring workers know how to act quickly and effectively.
Components of an Emergency Response Plan
- Evacuation procedures
- Emergency contact numbers
- Respiratory rescue equipment availability
- Regular drills and practice sessions
Training and Awareness
Training equips workers with the knowledge and skills to navigate confined spaces safely. Beyond initial training, fostering a culture of ongoing education benefits everyone. Regular refreshers and updates ensure that workers stay informed about new regulations and best practices.
In addition to formal training sessions, consider joining other professional development events. For instance, events like the Unlocking Your Potential Conference and the Mastering Your Time Conference are excellent opportunities for enhancing practical skills relevant to safe work practices.
FAQs
1. What are the primary hazards of confined spaces?
The primary hazards of confined spaces include chemical exposure, oxygen deficiency, and physical dangers from equipment or structures.
2. Is training required for all personnel working in confined spaces?
Yes, all personnel involved in confined space operations must receive proper training. This training includes understanding hazards, safety practices, and emergency response procedures.
3. What should I do if I detect a hazardous condition in a confined space?
If a hazardous condition is detected, evacuate immediately and alert the team outside. Follow the emergency response plan to ensure safety.
4. How often should training for confined space entry occur?
Regular training should occur at least annually, or more frequently if regulations change or new procedures are introduced.
Conclusion
In conclusion, confined space awareness and compliance are essential for maintaining workplace safety. Understanding the risks associated with confined spaces and implementing effective safety practices can significantly reduce potential accidents. Always remember the importance of training and communication in ensuring every worker knows the safest practices. To further develop your expertise, consider attending professional events such as the Safe Confined Space Entry, Awareness & Compliance Conference or the Premier Supply Chain Management Conference. Ultimately, fostering a culture of awareness and compliance within your organization promotes a safer work environment for everyone.